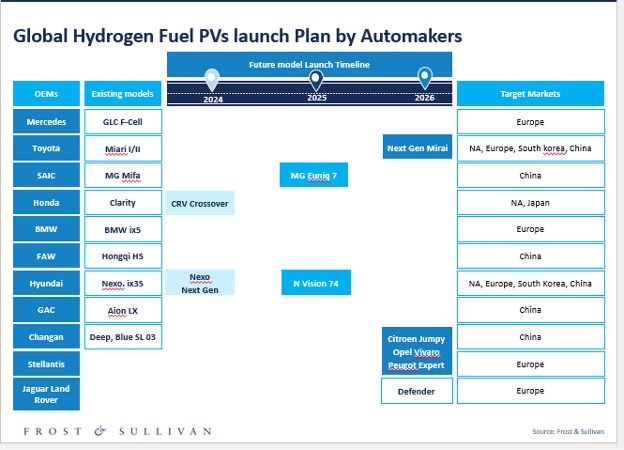
Biofuels, hydrogen, eFuels, and gas fuels are at the forefront even as commercialization success will hinge on hybrid integration, fuel technology innovation, cross-industry collaboration, and regulatory alignment.
As sustainability imperatives and energy security concerns intensify, the global automotive sector is undergoing a fundamental shift. While gasoline and diesel have historically dominated transportation, the industry is rapidly pivoting toward alternative fuels to reduce emissions and achieve carbon neutrality.
Electric powertrains have gained significant traction, even as a range of sustainable fuel alternatives, including biofuels, hydrogen, eFuels, and gas-based fuels, are emerging as complementary solutions. Regulatory mandates supporting cleaner fuels, along with advancements in fuel blending and ease of integration with existing infrastructure, will determine which of these technologies gains an edge.
Key Trends & Competitive Landscape
Challenges related to infrastructure compatibility and scalability notwithstanding, biofuels such as ethanol and biodiesel, as well as hydrogen-based solutions, are poised for rapid growth.
Driven by supportive policies, abundant feedstock availability, and a growing demand for sustainable transportation fuels, Brazil, Indonesia, India, and Malaysia are poised to be in the vanguard of biofuel development. Collectively, these countries are set to expand ethanol and biodiesel production by 10.6 million tons per annum (MTPA) and 7 MTPA, respectively. Biogas production is also witnessing strong growth, with two-thirds allocated for electricity and heating, with the remainder blended into gas networks or utilized as transportation fuel. Meanwhile, countries like Canada are setting ambitious hydrogen targets, with plans to generate 25 gigawatts (GW) of hydrogen by 2030 and achieve carbon-neutral hydrogen production by 2050, reinforcing global decarbonization efforts across industries, including transportation and heavy manufacturing.
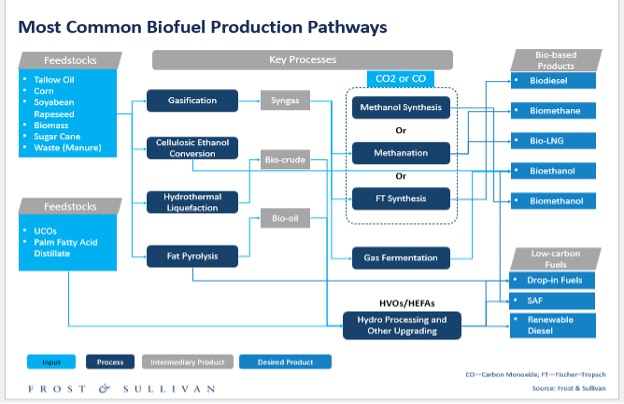
The alternative fuels market is highly competitive, with major energy corporations investing in various fuel technologies. Shell, Archer Daniels Midland, Green Plains, Neste, and Marathon Petroleum lead biofuel production, while companies like ExxonMobil, BP, Chevron, and TotalEnergies focus on gas fuels such as compressed natural gas (CNG) and liquefied petroleum gas (LPG). Hydrogen fuel development is particularly active, with Shell, Chevron, BP, Eni SpA, and Air Liquide spearheading initiatives in this space.
Notably, Shell has positioned itself as a dominant player in biofuels, producing 9.7 billion liters in 2023 through its joint venture with Raizen. Additionally, it has signed long-term agreements with Montana Renewables to expand its sustainable aviation fuel (SAF) supply chain. ExxonMobil is aggressively pursuing net-zero targets, with its Product Solutions division aiming to supply 40,000 barrels per day of lower-emission fuels by 2025, scaling up to 200,000 barrels daily by 2030. Eni SpA is also ramping up its sustainability strategy; it plans to double its bio-refining capacity to 2 MTPA by 2024, supported by a $0.75 billion annual investment in low-carbon fuel development.
To learn more, please access: Alternate Fuels in the Global Automotive Sector, 2024-2032, Top 10 Growth Opportunities for Alternative Fuels, 2025, CO2 Emissions Life Cycle in the Fuel Cell Electric Truck Sector, Europe, 2024-2040, or contact sathyanarayanak@frost.com for information on a private briefing.
Our Perspective
As the global automotive market steadily transitions toward alternative fuels, commercialization will be supported by hybrid integration and cross-industry collaboration. Automakers with a strategic focus on infrastructure investments, regulatory alignment, and fuel technology innovation will gain a competitive edge.
We expect expanding biofuels adoption in commercial fleets and heavy-duty vehicles by 2030, owing to their compatibility with internal combustion engine (ICE) infrastructure. This will drive increased investment in biofuel refineries and supply chains.
Between 2028 and 2035, industry-wide collaborations will facilitate the expansion of hydrogen and eFuel infrastructure, enabling automakers to scale their fuel cell and eFuel-powered vehicle portfolios. Hydrogen fuel cell technology, in particular, will become an appealing alternative for long-haul and commercial transport due to its rapid refueling times and extended range capabilities, compared to battery electric vehicles (BEVs). Moreover, innovations in green hydrogen production, such as electrolysis powered by renewable energy, and advances in hydrogen storage technologies, including cryogenic and solid-state solutions, will enhance feasibility while reducing costs.
Automakers can pursue a range of strategies to capitalize on alternative fuel integration. Strategic investments in modular vehicle architectures will allow manufacturers to integrate multi-fuel systems without compromising performance or safety.
For automakers, biofuels and eFuels present an immediate opportunity for existing ICE vehicles, allowing them to leverage their current manufacturing infrastructure without extensive modifications. Partnerships with the agricultural and waste management sectors can secure sustainable feedstock supplies, while advanced modeling software can aid in lifecycle assessments (LCA) to measure emissions and resource consumption across fuel pathways.
With hydrogen fuel cells likely to play a key role in commercial fleet electrification, manufacturers can develop hybrid models that integrate fuel cells with batteries. This approach will support improved efficiencies and attract a broader consumer base. Collaborating with renewable energy firms and green hydrogen start-ups will ensure a sustainable supply chain and lower costs.
Additionally, integrating alternate fuels with energy storage technologies, such as advanced batteries, will help create more flexible, hybrid solutions. This approach can help overcome constraints linked to inadequate charging station infrastructure that has hobbled the uptake of fully electric vehicles.
Alignment with government-led regulations, including clear incentives and investment frameworks, will be crucial to the commercial success of alternative fuels. On the one hand, local investments can mitigate risks associated with disrupted global supply chains in countries like Brazil, India, and the US, where biofuel production benefits from strong domestic feedstock supplies. Conversely, geopolitical instability in renewable energy-rich regions may slow eFuel production, compelling automakers to diversify sourcing strategies.
With inputs from Amrita Shetty, Senior Manager, Communications & Content –Mobility