Strategic partnerships, infrastructure expansion, battery swapping, battery-as-a-service (BaaS) initiatives, and a focus on innovation and affordability will spark boom in India’s e2W market.

India’s electric two-wheeler (e2W) market has experienced remarkable growth in recent years, driven by government support and a shift toward sustainable transportation. Policy initiatives, such as the Faster Adoption and Manufacturing of Hybrid and Electric Vehicles (FAME-II) scheme have offered subsidies and tax breaks to boost e2W sales, even as consumers have embraced cleaner alternatives to traditional fuel-powered vehicles. However, recent policy adjustments have slowed market growth as the government aims to build a self-sustaining electric vehicle (EV) ecosystem that can thrive without relying heavily on subsidies.
Despite the slowdown, the long-term outlook for India’s e2W market remains buoyant. As technological advancements continue and production costs decrease, manufacturers and investors are well-positioned to capitalize on growing demand. Established players, such as Hero MotoCorp and Bajaj, are competing with newer entrants like Ather Energy and Ola Electric, creating a dynamic market environment. Competition is expected to accelerate innovation, particularly in battery technology and vehicle range, providing consumers with an increasing variety of affordable e2W options.
To learn more, please access: Indian Electric Two-Wheeler (e2W) Market, Forecast and Growth Opportunities, 2024–2030, Growth Opportunities in Connectivity Technology in the Two-wheeler Market, 2024-2028, Global Two-wheeler Growth Outlook 2024, and Strategic Analysis of Battery Chemistries in Electric Two-wheelers and Growth Opportunities, or contact [email protected] for information on a private briefing.
Government Support and Investments Create Growth Momentum
One of the primary drivers of India’s e2W market are government schemes such as FAME-II and the Electric Mobility Promotion Scheme (EMPS) 2024 that provide subsidies and incentives to manufacturers and buyers with a view to realizing an 80% e2W market share by 2030. The introduction of revised EV policies and incentives, such as battery swapping initiatives—that reduce downtime and alleviate range anxiety—have aimed to further boost EV adoption. With a focus on expanding charging infrastructure and encouraging Battery-as-a-Service (BaaS), both the government and private sector are working together to create a robust ecosystem that supports widespread e2W usage.
Investment in the sector has also been significant, with startups such as Ather Energy, Ultraviolette, and River attracting substantial equity funding. This influx of capital is enabling companies to scale operations, enhance their product offerings, and develop new technologies. Moreover, partnerships between automakers and tech companies are accelerating the development of charging networks and battery swapping solutions, which will be essential for the continued expansion of the e2W market.
While the Indian e2W market is growing, several challenges persist. The most significant is range anxiety, as many potential buyers are concerned about the limited availability of charging stations, particularly in rural and Tier III or IV cities. Although the government and private players, such as Sun Mobility, Battery Smart, Gogoro, and Ather Grid, are committed to expanding the charging network, progress has been slower than anticipated. This lack of infrastructure remains a key barrier to widespread adoption.
Another challenge is the higher production cost of EVs compared to their ICE counterparts. Although government subsidies have helped offset these costs, domestic manufacturers still face difficulties in sourcing affordable components. Many critical parts, such as lithium-ion batteries, are imported, which drives up production expenses. Until India develops a robust domestic EV component supply chain, lowering costs will remain a challenge for e2W manufacturers.
Competitive Landscape and Innovation
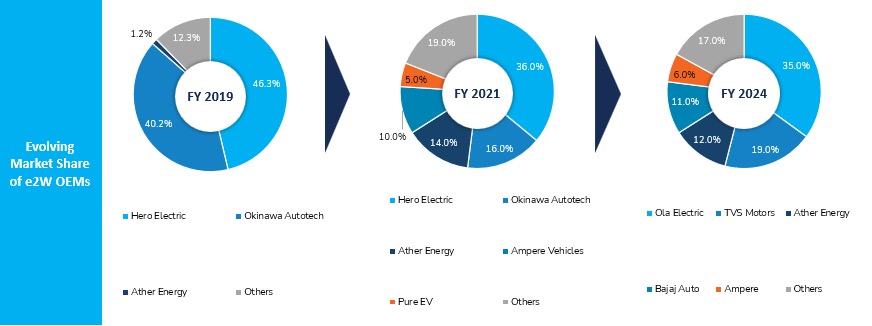
India’s e2W market is highly competitive, with both established players and startups vying for market share. In 2024, Ola Electric emerged as the clear leader, with TVS, Ather, Bajaj, and Ampere rounding out the top five manufacturers. This competitive environment has spurred rapid innovation in areas such as battery range, performance, and features. High-speed electric scooters, which offer superior performance and longer ranges, are gaining popularity, reflecting a shift in consumer preferences toward more powerful and efficient e2Ws.
Technological advancements in embedded telematics, fast-charging capabilities, and vehicle-to-everything (V2X) communications are also driving the evolution of the e2W market. Features like removable batteries, touchscreen displays, and intelligent personal assistants (IPAs) are becoming increasingly common, making e2Ws more convenient and user-friendly. As a result, these innovations are accelerating the adoption of e2Ws, particularly in urban areas where consumers value convenience and connectivity.
Our Perspective
Looking ahead, we expect the Indian e2W market to continue its upward trajectory, with a projected compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 41.9% from FY 2025 to FY 2030. To realize this potential, automakers will need to focus on strategic partnerships, localized production, and innovation. Collaborating with state governments, battery manufacturers, and charging infrastructure providers will be crucial in developing a sustainable EV ecosystem. Targeting specific customer segments, such as rural populations or performance-oriented riders, through tailored marketing campaigns and product offerings will also be essential.
The shift from traditional retail models to direct-to-consumer sales, as seen with Ola Electric, is another emerging trend. By adopting subscription-based services or online sales platforms, automakers can reduce infrastructure costs and reach a broader customer base. Subscription models offer a recurring revenue stream while enabling companies to maintain control over sales, service, and customer relationships. However, these models come with their own set of challenges, including the need for significant capital investment and dedicated management to ensure customer satisfaction.
Lastly, diversification will play a key role in the long-term success of India’s e2W market. Manufacturers must explore new revenue streams beyond vehicle sales, such as BaaS models, data monetization, and connected vehicle services. Additionally, battery recycling presents a lucrative opportunity for companies to capitalize on the growing demand for sustainable solutions. By embracing these strategies, e2W manufacturers can transform from vehicle producers into comprehensive mobility providers, securing a competitive edge in the evolving market.
The Indian e2W market is at a critical juncture. By focusing on affordability, innovation, and strategic partnerships, stakeholders can unlock new revenue opportunities and lead the charge in India’s transition to electric mobility.
With inputs from Amrita Shetty, Senior Manager, Communications & Content –Mobility