Prismatic, cylindrical, and pouch cells vie for dominance as multi-format, multi-chemistry manufacturing strategies and technology-agnostic facilities become progressively crucial.
The increasing adoption of electric cars and stricter environmental policies are accelerating global demand for electric vehicle (EV) batteries. The EV battery market is, meanwhile, undergoing profound transformation propelled by new cell formats, chemistries, and production strategies. Competing cell types—cylindrical, prismatic, and pouch—are vying for dominance. At the same time, breakthroughs in lithium-ion technology, solid-state batteries, and alternative battery chemistries are redefining the market landscape. With an intensified focus on achieving higher energy density, faster charging capabilities, and enhanced safety features, the EV battery market is on the brink of rapid change.
Prismatic cells at the forefront
Rising EV adoption is projected to result in annual global EV battery installations of 3,177 GWh by 2030. In their bid to gain market leadership, participants are evaluating alternative chemistries, enhancing existing formats, and exploring the potential of novel material states. At the forefront of such initiatives are technologies such as silicon anode, lithium-sulfur, and solid-state batteries. Among these, solid-state batteries are anticipated to achieve widespread adoption by 2030. Efforts to improve battery performance, while minimizing reliance on critical raw materials, will highlight developments in all-solid-state batteries and larger cell formats.
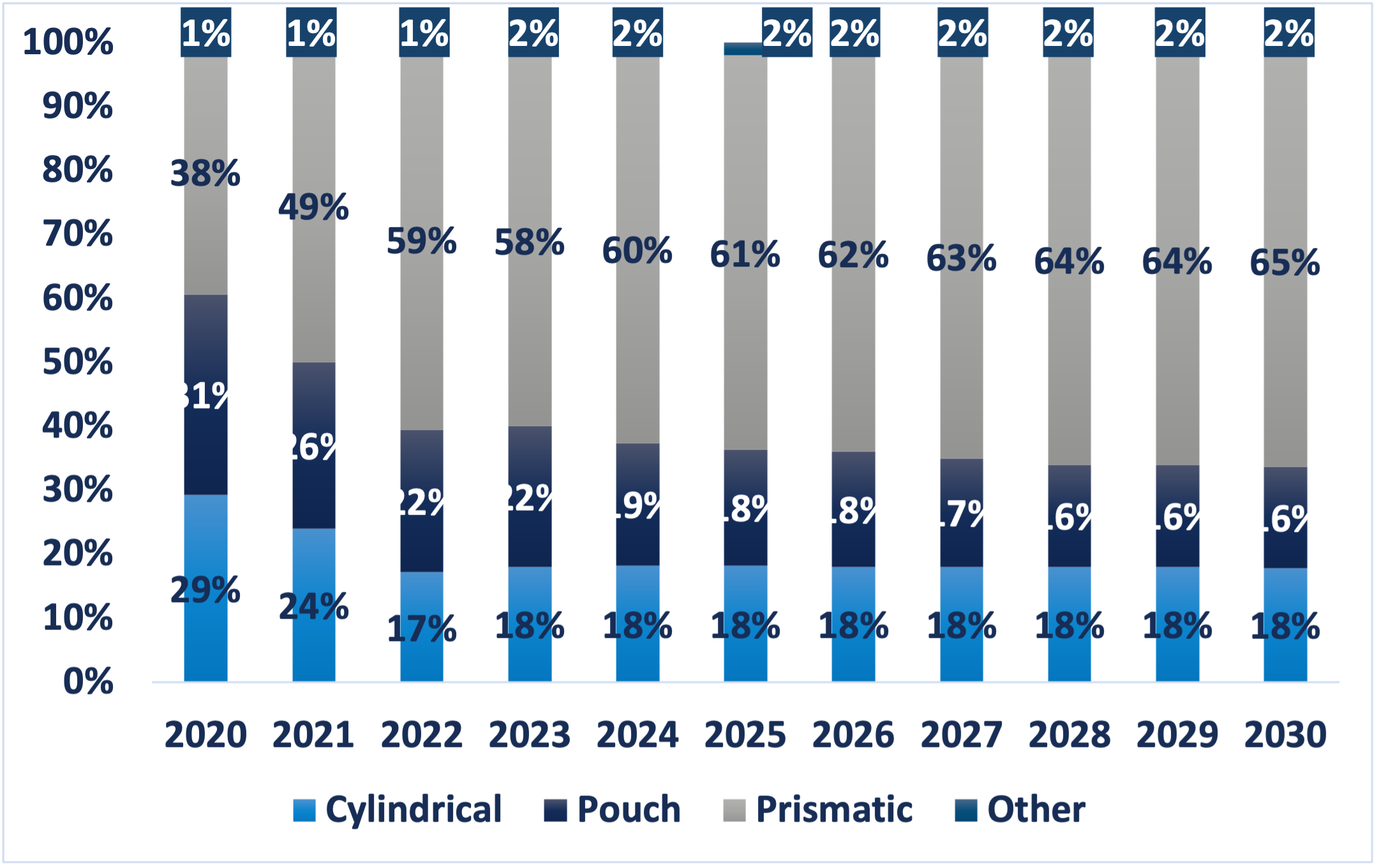
Estimated Percentage Market Share of Cell Formats, Global (2021-2030)
Source: Frost & Sullivan
Among the major EV battery cell types, prismatic cells currently dominate due to their high energy density, efficient packaging, and superior thermal management. These characteristics make them a preferred choice for manufacturers. Among key EV markets, China is the largest consumer of prismatic cells followed by Europe and North America. Backed by their compatibility with current and emerging chemistries, prismatic cells are poised for accelerated growth and are set to capture around 65% market share by 2030.
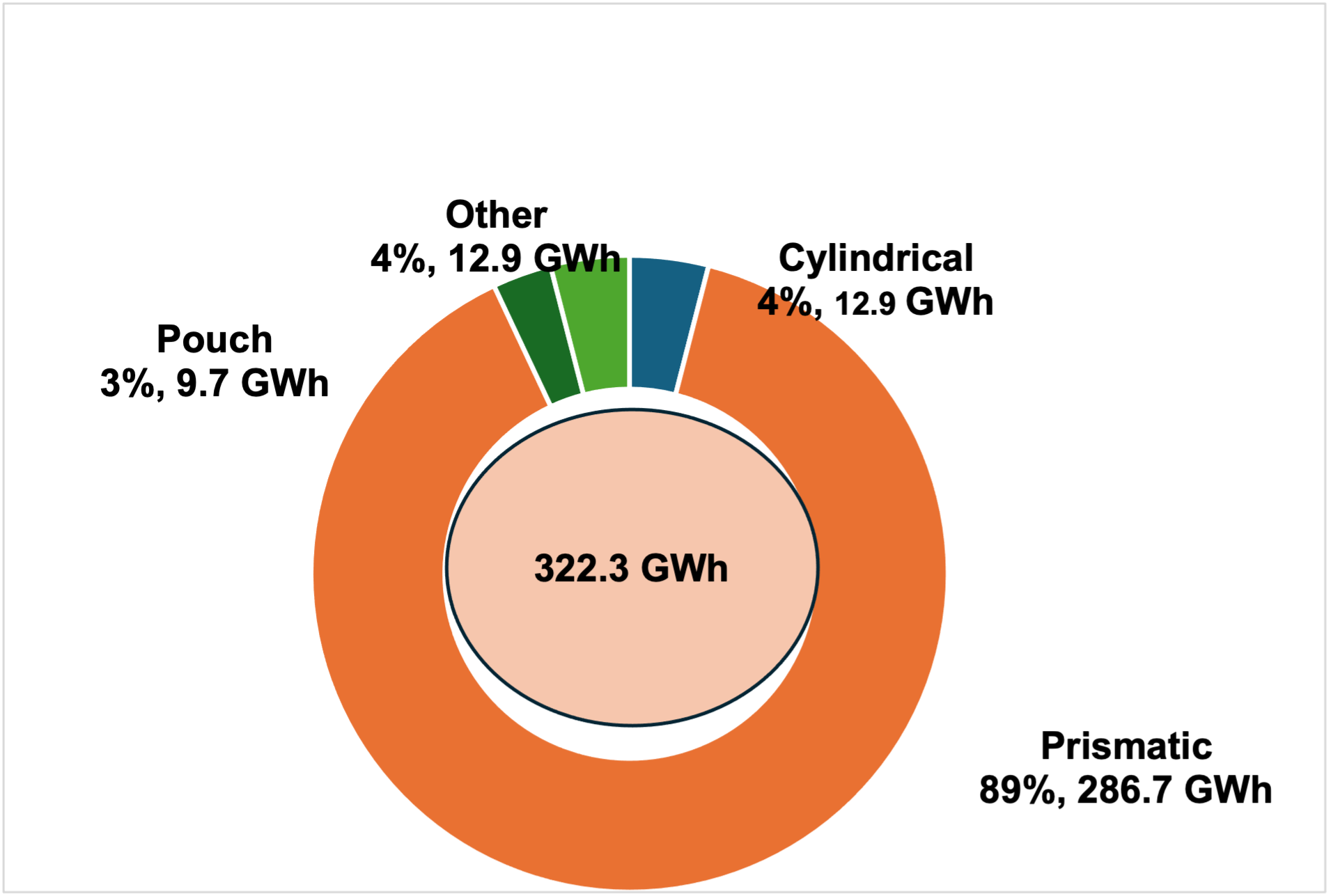
EV Batteries: Market Share by Cell Format, China (2023)
Source: Frost & Sullivan
In parallel, cylindrical and pouch formats are also gaining traction in specific applications. By 2030, the demand for cylindrical cells is expected to grow due to the rising adoption of lithium iron phosphate (LFP) batteries in standard vehicle models. Cylindrical cells currently dominate the Americas market, driven by Tesla EVs that use cylindrical batteries. By the end of this decade, they will account for an estimated 18% market share, closely followed by pouch cells which will benefit from the expanding adoption of solid-state batteries.
China remains the leading global producer of EV batteries, with key players such as CATL, BYD, and CALB. In 2023, it led the global EV battery market with 322.3 GWh of installations out of a global total of 594.4 GWh. South Korean manufacturers, including Samsung SDI and LG Energy, and Japan’s Panasonic are also prominent players. Investments in high energy density and safety-focused batteries are driving innovations that will likely see the adoption of new chemistries, advanced battery pack designs, and alternative cathode and anode materials by 2030.
To learn more, please see: Evolution of EV Batteries by Cell Type (Prismatic, Pouch, Cylindrical), Forecast to 2030, Growth Opportunities in the BaaS Market, 2024-2030, and Strategic Analysis of Battery Chemistries in Electric Two-wheelers and Growth Opportunities or contact [email protected] for information on a private briefing.
Our Perspective
Amid rapid market evolution, stakeholders will need to adopt comprehensive strategies encompassing multiple cell formats, diverse chemistries, and adaptable production facilities. These measures will ensure resilience, cost efficiency, and competitiveness.
EV automakers should integrate a combination of cylindrical, prismatic, and pouch cells and customize battery packs to cater to varying vehicle segments and performance requirements. This approach will enable tailored performance for specific vehicle models. It will, furthermore, reduce dependency on a single supplier, thereby mitigating risks related to supply chain disruptions. And, lastly, it will help align production expenses with specific market and vehicle segment needs.
Similarly, battery cell manufacturers must diversify their chemistries to safeguard against supply chain risks and optimize costs. Incorporating multiple chemistries will reduce reliance on specific materials and suppliers, while enhancing cost efficiency by leveraging varying production costs across chemistries. This strategy will also ensure technological flexibility, facilitating the integration of emerging battery technologies without major disruptions.
Production flexibility will be a key criterion for success. Facilities capable of producing various cell formats, chemistries, and solid-state batteries will be better positioned to adapt to market changes. Designing gigafactories with modular layouts for diverse production processes, incorporating robust material handling systems, and using technology-agnostic equipment will enable manufacturers to stay ahead of trends and adapt swiftly to new technologies.
With inputs from Amrita Shetty, Senior Manager, Communications & Content – Mobility