Leading automakers are tailoring C.A.S.E. strategies to accommodate regional dynamics, while accelerating the transition to a sustainable, efficient, and consumer-focused mobility ecosystem.
Global automakers are pursuing Connected, Autonomous, Shared, and Electric (C.A.S.E.) strategies, adapting to regional priorities and challenges while simultaneously leveraging these strategies to shape a sustainable, efficient, and consumer-focused mobility ecosystem.
Connected vehicles (CVs) are a cornerstone of this shift, offering enhanced safety, security, and convenience through real-time data exchange with external systems. Autonomous vehicle (AV) technology continues to progress, although fully self-driving vehicles (Level 5 autonomy) face significant technological and ethical challenges. Meanwhile, the trend toward shared mobility is gaining traction, especially among younger generations who value access over ownership. Electrification, another critical pillar, sees mixed enthusiasm across the industry, but investments in electric vehicle (EV) technology are substantial as OEMs push toward fleet electrification.
To learn more, please access: CASE Strategies of OEMs which profiles 6 global automotive OEMs based on their CASE mobility strategies, including General Motors. Ford, BMW, Volkswagen, Toyota, and Honda, or contact [email protected] for information on a private briefing.
Fierce Competition and Sustainability Imperatives Shape the Market
Environmental concerns are reshaping consumer preferences, compelling automakers to focus on cleaner energy, sustainable materials, and battery recycling. Stricter emissions and safety regulations are spurring advances in electric and autonomous vehicles, with OEMs innovating to meet these standards. Sustainability considerations are increasingly being integrated into connected systems, fostering a more eco-friendly and connected transportation landscape.
Fierce competition is accelerating innovation, particularly in connected car features, autonomous driving, and vehicle electrification. Pure-play EV makers and traditional OEMs are locked in a race, with new entrants from Asia disrupting the market with competitive pricing. Partnerships, acquisitions, and strategic alliances are becoming essential for OEMs to stay ahead, as they strive to balance cost efficiency and differentiation.
Meanwhile, the lines between automakers and tech companies are blurring. AI, software, and advanced materials are now integral to automotive design, with carsharing and subscription models challenging traditional ownership. As automakers collaborate with telecom and tech firms, new in-car experiences and connected services are emerging, while cybersecurity, inadequate infrastructure, and evolving regulations remain key challenges to widespread C.A.S.E. adoption.
Regional Roadmaps
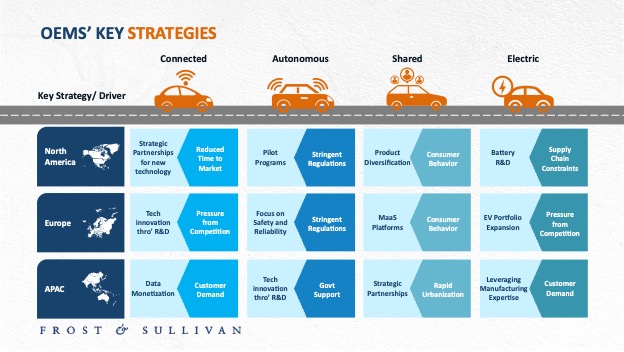
In North America, automakers are heavily investing in CV technologies, prioritizing driver experience and convenience through advanced connectivity features. These vehicles serve as platforms for integrating cutting-edge technologies, such as real-time data exchange, enhanced user interfaces, and seamless infotainment systems. While the focus remains on enriching the driving experience, cybersecurity, and data privacy have emerged as major concerns, prompting OEMs to build robust defenses against hacking and data breaches.
Europe is at the forefront of connected mobility, with around 75% of vehicles expected to be connected by 2026. Safety and sustainability are driving forces, supported by collaborative efforts within the European Union to standardize connected technologies and establish 5G corridors across the region. However, strict regulations like the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) continue to present hurdles, as automakers work to balance innovation with rigorous data privacy requirements.
In Asia, connected vehicle development is gaining momentum, though the market remains in its early stages. Automakers in the region are focusing on meeting local infrastructure limitations and consumer needs, often partnering with local tech companies and telecom providers to enhance connectivity features. Countries like China and Japan are making strides in this space, with efforts tailored to the specific demands of dense urban environments and high-traffic areas, setting the stage for future growth in CV adoption.
OEMs in North America are aggressively pursuing EV development, driven by government incentives, falling battery prices, and growing consumer interest. The market in the region is highly competitive, with traditional OEMs, new entrants, and Asian companies focusing on electric SUVs and trucks, supported by investments in charging infrastructure. Europe leads in EV adoption due to stricter emission regulations and incentives, with a focus on hatchbacks and compact SUVs. In Asia-Pacific, hybrid EVs, electric two-wheelers, and small, affordable EVs dominate, though Japanese companies like Toyota have been slower to enter the market. Despite issues related to infrastructure and government support, China leads with its array of EV offerings.
AV technology is advancing globally, but regional differences are notable. In North America, OEMs are nearing Level 4 autonomy, though full implementation is being delayed by stringent safety regulations and the need for further testing. Europe’s cautious approach focuses on safety, with public reluctance slowing AV adoption despite heavy investments. In contrast, Asia Pacific, particularly China, is pushing ahead with government support, extensive testing, and city environments well-suited for autonomous ride-hailing services. Across all regions, shared mobility initiatives, especially in Europe and Asia, are closely linked to AV development, as automakers explore new business models in a rapidly evolving transportation landscape.
Our Perspective
CV services are a key focus for all OEMs. Automakers are enhancing cloud infrastructure and data management to offer services like usage-based insurance (UBI), in-vehicle infotainment (IVI), and AI-based virtual assistants. Proprietary operating systems and mobile apps are becoming integral to connected car ecosystems, providing seamless user experiences. Future developments in intelligent personal assistants and vehicle-to-everything (V2X) technology will further drive innovation in this space.
In autonomous mobility, stringent regulations and safety concerns are determining the pace of development, particularly in North America and Europe. BMW and General Motors face challenges in pushing Level 4 AVs to market. However, China is emerging as a key testing ground for fully self-driving vehicles, which are expected to see commercial deployment by 2026, initially for highway driving and parking.
Shared mobility remains underdeveloped for most OEMs, with Volkswagen being an exception. Shared mobility initiatives, however, serve as a testing platform for AV technologies. Micromobility, particularly in urban areas, is gaining traction through partnerships, offering potential for alternative revenue streams.
EVs represent a major focus for companies like Volkswagen, GM, and BMW, all of which have robust EV portfolios. In contrast, Japanese automakers like Toyota have been slower in embracing fully electric models, with limited lineups. While concerns about battery life cycles and macroeconomic factors persist, automakers are setting aggressive goals to ensure they remain competitive in the EV space, as the transition to vehicle electrification becomes increasingly inevitable.
As automakers look to a C.A.S.E future, growth opportunities will be fueled by the integration of V2X technology, which will enhance in-car services and open up new revenue streams. Subscription services for advanced safety features, real-time traffic updates, and personalized experiences powered by V2X data will present further potential for growth.
Another key opportunity will lie in the convergence of autonomous and shared mobility. Shared AVs will accelerate EV adoption and foster new business models, such as subscription-based access to AV fleets, eliminating the need for personal car ownership and enabling on-demand services like deliveries or mobile workspaces.
With inputs from Amrita Shetty, Senior Manager, Communications & Content – Mobility