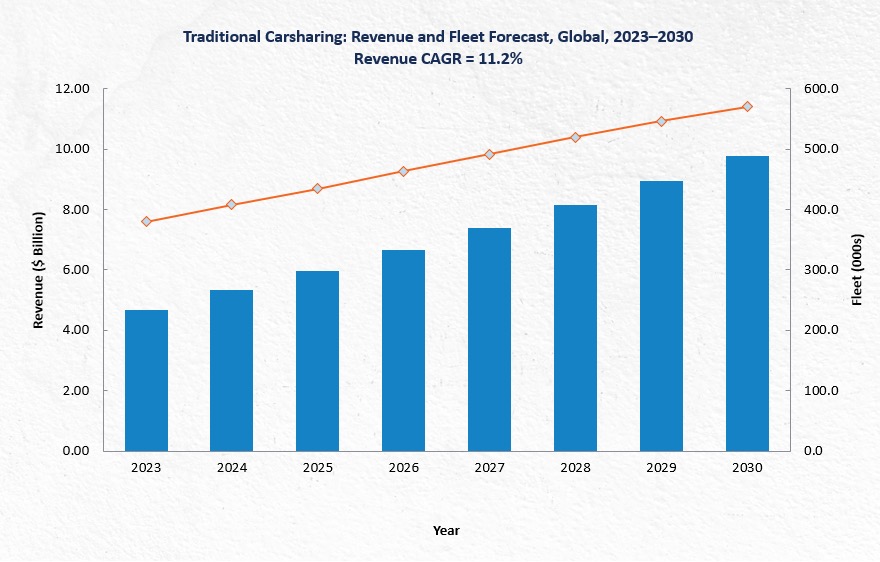
The global carsharing industry is entering a new phase of evolution, influenced by urban development trends, environmental regulations, and technological advancements. As cities increasingly access regulations, and zero-emission targets, carsharing is emerging as a critical component of urban mobility. With the global carsharing market projected to grow from $4.66 billion in 2023 to $9.79 billion by 2030, operators are shifting their focus from expansion to profitability.
Traditionally, carsharing has been a mature market, with operators heavily investing in scaling operations across various regions. However, the landscape is changing as operators recognize the need to enhance operational efficiencies to achieve profitability. To stay competitive, companies are now exploring niche markets and specialized applications, such as airport carsharing, real estate-oriented services, and business carsharing. Additionally, integrating advanced technologies like intelligent fleet management systems and predictive maintenance is becoming crucial for sustaining growth and profitability.
Cities that prioritize sustainable transportation play a vital role in accelerating carsharing adoption. Incentives such as designated parking spaces, subsidies, and favorable regulations are pivotal in encouraging the use of shared mobility. Moreover, carsharing is poised to become an integral part of Mobility as a Service (MaaS) platforms, further embedding it into the urban mobility ecosystem and enhancing its appeal to city dwellers.
To learn more, please access: Growth Opportunities in Global Traditional Carsharing, 2024-2030, Global Shared Mobility Predictions and Outlook, 2024, European and North American Mobility-as-a-Service Growth Opportunities, Growth Opportunities in the Evolving Public Transport Landscape, 2030, and Evolution of Shared Mobility Infrastructure in Top 20 Smart Cities, or contact [email protected] for information on a private briefing.
Emphasis Shifts from Expansion to Profitability
The carsharing industry, which has been in existence for over 15 years, is now focusing on profitability after years of aggressive expansion. Operators are consolidating their operations by scaling back from less profitable regions and concentrating on markets where they can achieve sustainable growth. Notable examples include companies like Zity in Paris, Spark in Romania, and Eloop in Vienna, which have refocused their efforts on core regions to achieve their profitability targets. Singapore’s GetGo, for instance, reported profitability for the second consecutive year in 2023, with revenue growth exceeding 300%.
The transition to electric vehicles (EVs) fleets is gaining momentum in the carsharing sector as cities impose stricter zero-emission targets. Operators are increasingly incorporating EVs into their fleets to comply with these regulations, with smaller electric carshare programs emerging in local communities, universities, and residential areas. Innovative examples include MyWheels, which introduced a bidirectional charging fleet capable of receiving power from charging stations and returning it to the grid when needed. This trend underscores the growing importance of electrification in meeting environmental goals and enhancing the sustainability of carsharing services.
Once considered a niche market, residential carsharing is gaining traction globally. Specialized operators that cater exclusively to residential communities are emerging, offering real estate developers the opportunity to reduce property and rental prices by eliminating the need for parking spaces. Companies like Ohmie Go, Outbound, and EV Mobility are leading the way in this space. Even luxury automakers like Jaguar are exploring residential carsharing, piloting schemes for residents of exclusive apartments in the UK.
Additionally, technology will play a central role in the shift toward profitability. Operators are increasingly leveraging safety-related technologies, predictive maintenance, and fleet optimization tools to improve operational efficiency and reduce costs. Vulog’s technology platform, used by Leo&Go, helped the operator achieve profitability within 21 months of launching with a fleet of just 300 cars, demonstrating the potential of technology to transform the industry.
Regional Market Dynamics
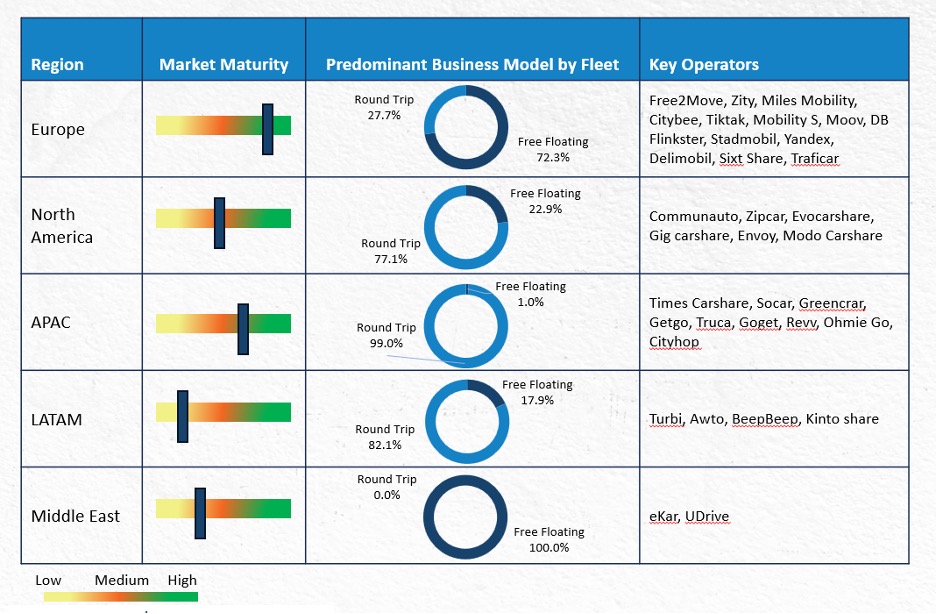
The global traditional carsharing market has witnessed a significant increase in demand after the COVID-19 pandemic. In North America, the sector has experienced a decline in free-floating carsharing due to unfavorable parking regulations in urban areas. However, station-based carsharing is on the rise, particularly in Canada, where Communauto is expanding its operations.
Europe has seen a consolidation of carsharing operations, with companies like Free2Move focusing on profitable regions with higher demand and supportive regulations and scaling back in less viable markets. The growth of community-based carsharing, especially in rural areas, is expected to continue, driven by the increasing adoption of electric fleets.
In contrast, the Chinese carsharing market is experiencing a downturn as operators shift toward short-term rental services due to declining demand. Similarly, in India, Zoomcar, once a dominant player in the market, has transitioned to a marketplace model, stabilizing fleet growth in the process. Despite challenges, the South Korean market continues to expand, with Socar leading due to its extensive user base and national presence.
Our Perspective
Globally, operators will aim to achieve profitability through multiple means, such as consolidating regions, increasing utilization rates, using AI-based technologies, and electrifying fleets.
To capitalize on the opportunities presented by these trends, carsharing operators must focus on integrating new technologies that enhance profitability and user experience. Carsharing operators must prioritize user experience by developing mobile apps with seamless keyless entry, real-time information on vehicle availability and charging stations, and personalized recommendations. Carsharing should invest in analytics capabilities to leverage data for real-time pricing adjustments, fleet rebalancing, and predictive maintenance.
Electrification offers significant growth potential, particularly in attracting environmentally conscious consumers and reducing operational costs. However, realizing these benefits will require time and investment in infrastructure, such as charging stations and grid integration. Cities can play a critical role in this transition by offering tax incentives and subsidies to encourage the adoption of electric fleets.
Finally, as carsharing becomes increasingly integrated into multimodal platforms, operators should explore partnerships with other mobility providers, including micromobility modes like bike-sharing and e-scooter companies, to create a comprehensive mobility ecosystem. By offering users a wider range of transportation options, carsharing can position itself as a key player in the future of urban mobility.
With inputs from Amrita Shetty, Senior Manager, Communications & Content – Mobility