As known attacks fade away, Threat Intelligence remains one of the top three investment priorities in IT security for Indian companies. Over the last few years and specifically during the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic, enterprises have constantly been bombarded with advanced and unknown threats that they are not equipped to deal with. Suddenly, employees had to be shifted to work-from-home due to a nation-wide lockdown. Due to lack of preparedness, confidential databases, endpoint devices, and cloud workloads have been targeted resulting in ransomware attacks and data thefts. Most of the attacks are voluminous, targeted, multi-vector, polymorphic, signature-less, and importantly unknown; making it challenging for enterprises to prevent these attacks. Hence is the need for a cybersecurity framework that leverages threat intelligence and can identify and respond to advanced threats thereby creating an improved security posture.
As known attacks fade away, Threat Intelligence remains one of the top three investment priorities in IT security for Indian companies. Over the last few years and specifically during the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic, enterprises have constantly been bombarded with advanced and unknown threats that they are not equipped to deal with. Suddenly, employees had to be shifted to work-from-home due to a nation-wide lockdown. Due to lack of preparedness, confidential databases, endpoint devices, and cloud workloads have been targeted resulting in ransomware attacks and data thefts. Most of the attacks are voluminous, targeted, multi-vector, polymorphic, signature-less, and importantly unknown; making it challenging for enterprises to prevent these attacks. Hence is the need for a cybersecurity framework that leverages threat intelligence and can identify and respond to advanced threats thereby creating an improved security posture.
What is Cyber Threat Intelligence?
Cyber threat intelligence refers to an organization’s ability to prevent or mitigate cyber-attacks. Enterprises use intelligence products and services built on evidence-based knowledge to prepare, prevent, and identify known and unknown cyber threats by leveraging on reliable resources. Threat intelligence aggregates, correlates, and analyzes threat data from multiple sources to create an improved defense mechanism.
The need for threat intelligence is to build:
- Proactive and predictive security posture (not reactive) within enterprises
- Improved threat detection and faster remediation and mitigation
- Better decision making during and after a cyber intrusion
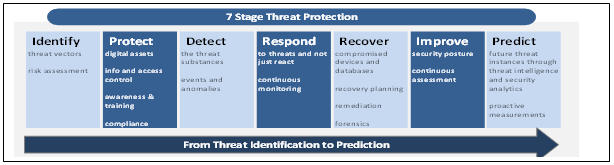
The Role of Threat Intelligence in 7 Stage Threat Protection
Today, enterprises need a 360-degree security framework that protects digital assets, workloads, and endpoints. This framework needs to be banked on proactive security architecture with threat intelligence as its backbone. Frost & Sullivan strongly believes the current cybersecurity architecture for enterprises needs to be restructured to the needs of modern cyber threats and built on the 7 Stage Threat Protection.
Exhibit 1: 7 Stage Threat Protection
Source: Frost & Sullivan
The 7 Stage Threat Protection uses threat intelligence products to address three key areas:
- Enrich other security technologies
- Vulnerability prioritization
- Open, deep, and dark web monitoring

The intelligence solution inspects the open sources (publicly available data on the internet), deep web (data which is locked behind the secure logins or paywalls), and dark web (data on the internet that is encrypted and used in trading illegal goods or services) to protect data everywhere it resides.
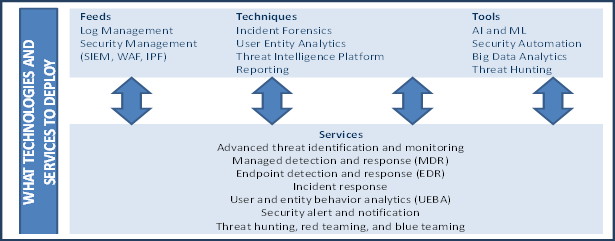
How to Build Cyber Threat Intelligence
There is no single product that provides complete end-to-end threat intelligence against all types of cyber-threats. Rather, threat intelligence is a collection of security technologies and tools that work hand-in-hand with each other to provide event correlation, threat monitoring, and incident response in real-time. While SIEM has been the core of the threat intelligence structure for enterprises for several years, when it comes to identifying unknown attacks, enterprises need the ability to capture and act upon the right security information. Advanced security technologies like Incident Forensics, User Entity Analytics, and Threat Intelligence Platform work in tandem with Log Management and Security Management (like SIEM) to deliver the best possible proactive security outcome. Most of these tools and techniques are empowered with next-generation technologies like artificial intelligence, machine learning, big data analytics, and robotics process automation that are most effective against non-signature and file-less threat actors. To combat modern cyber threats, enterprises need to take advantage of forward-looking security services like Managed Detection and Response (MDR), Advanced Threat Identification, Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR), Threat Hunting, and Red/Blue Teaming Services.
Exhibit 2: What Technologies and Services to Deploy
Source: Frost & Sullivan
Industry Verticals Benefiting the most from Cyber Threat Intelligence

IT/ITeS: India is a destination for several large technologies and outsourcing firms. Each of these companies becomes a massive customer data repository globally. Hackers are constantly on the lookout to target and steal sensitive customer information. Of late, ransomware attacks have become common incidents across the IT and ITeS companies apart from zero-day attacks and phishing campaigns. Most outsourcing companies have already realized the need to invest in updated next-generation security technologies and concepts like MDR, User and Entity Behavior Analytics (UEBA), e-discovery, incident response, dark web monitoring, and forensics which are intelligence-driven and help enterprises stay ahead in the race against cyber-attacks.

The Way Ahead in Cybersecurity
Threat intelligence is soon expected to become fundamental to cyber defense. As security incidents escalate daily and cybersecurity becomes the No.1 priority for businesses, enterprises need to invest and adopt security technologies that are contextual, behavior-driven and cater to future needs. Legacy security tools would cease to exist, making way for intelligence-based cybersecurity products – something enterprises have long been looking towards.